Myringoplasty
What are the benefits of surgery?
Surgery can prevent repeated ear infections and sometimes improve hearing.
Are there any alternatives to surgery?
Keeping the ear dry by placing cotton wool and Vaseline in the ear when bathing or washing your hair may prevent infection.
An infection can be treated with antibiotics and a trained healthcare practitioner can clean the ear. A hearing aid can improve poor hearing.
What does the operation involve?
A myringoplasty is usually performed under a general anaesthetic but a local anaesthetic can be used. The operation usually takes between an hour and an hour and a half.
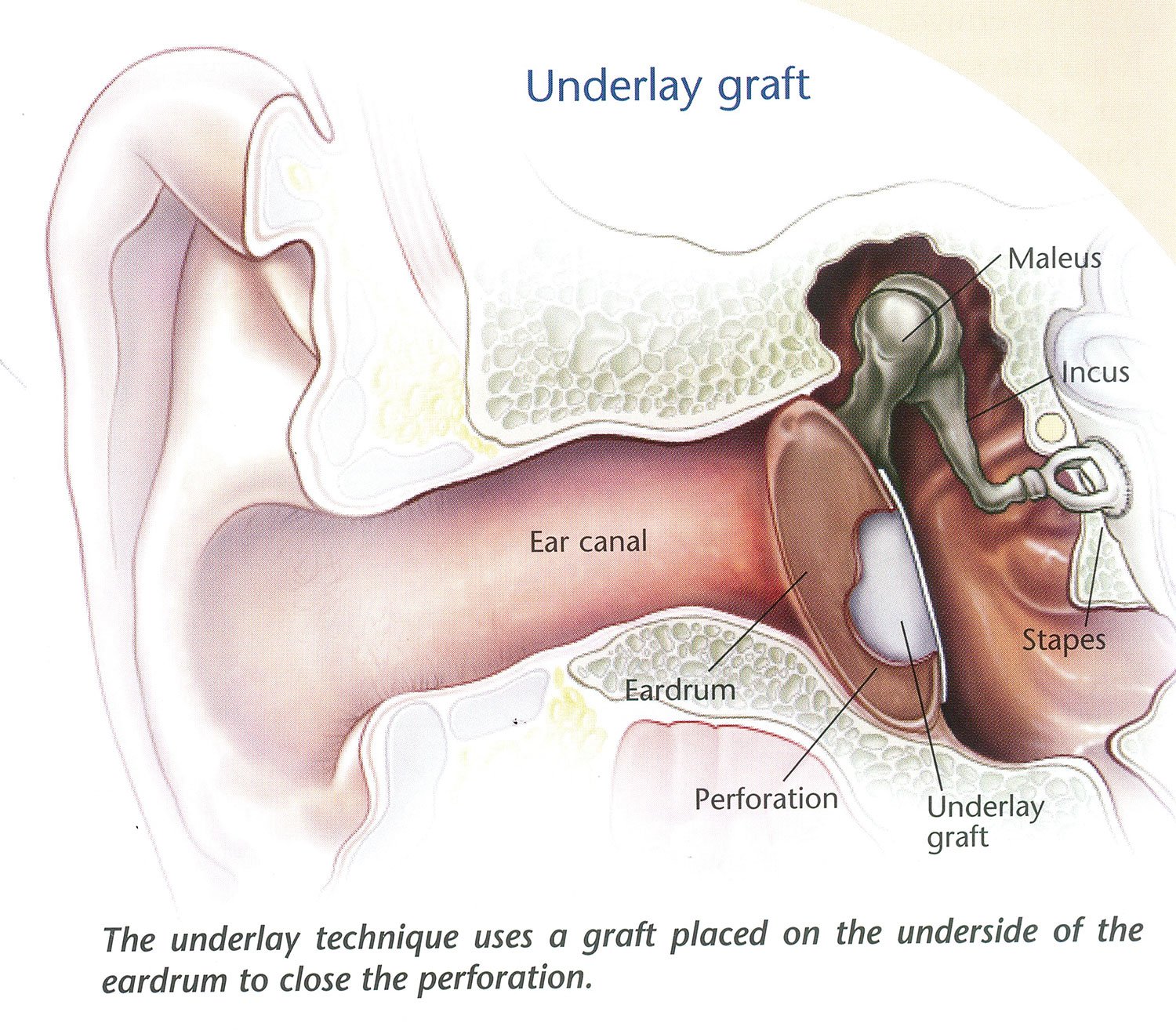
Your surgeon will need to use a graft (piece of tissue) to cover the hole.
Your surgeon will insert the graft through a cut made either in front of or behind your ear or inside your ear canal. They will lift the eardrum and place the graft underneath it and support it with a dissolving sponge. They will then put the eardrum back.
What complications can happen?
1 General complications
Pain
Bleeding
Infection of the surgical site (wound)
Unsightly scarring
Blood clots
2 Specific complications
Failure of the graft
Loss of hearing
Tinnitus
Change of taste
Allergic reaction
How soon will I recover?
You may be able to go home the same day. If a head bandage has been used, it will be removed the morning after surgery.
Your surgeon will tell you when you can return to normal activities. You should stay off work for two weeks.
Regular exercise should help you to return to normal activities as soon as possible. Before you start exercising, you should ask a member of the healthcare team or your GP for advice.
You will need to come back two to three weeks after the operation to check the graft.
A myringoplasty is an operation to repair a hole (perforation) in the eardrum. A perforation is usually caused by an infection in the middle ear that bursts through the eardrum. It can also be caused by trauma (for example, being hit across the ear). A perforated eardrum can lead to repeated ear infections and poorer hearing.